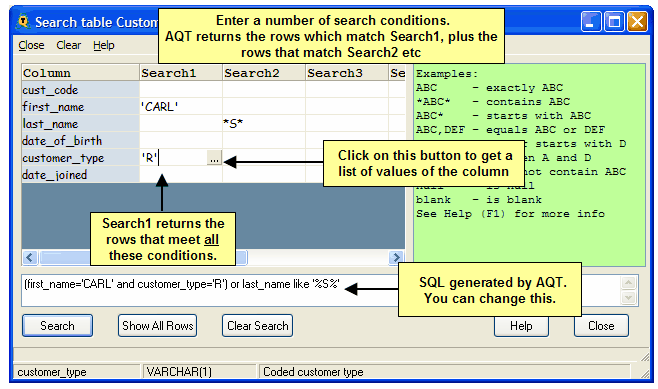
The Search Table window provides a quick way or building a simple search on a table. It can be invoked in one of the following ways:
or clicking on the Table Search icon ![]() .
.
The Table Search function operates slightly differently in these three cases:
When the Search Table window is opened, it will display all the columns in your table.
AQT remembers the search conditions you specified the last time you used the window. If the table name hasn't changed, these remembered search conditions will be filled out on the window.
When you invoke Search Table from the Data Display window, the cell you have selected in the Data Display window will be set up in Search Table as a search condition. You can use this feature to search for a particular column value with a few clicks.
AQT allows you to enter 5 searches. Each search will return a set of rows. If you specify two searches, you will see all the rows which meet Search1 plus all the rows which meet Search2 (from an SQL point of view, the searches are ORed).
Each search consists of a set of conditions on columns in the table. The search will only display rows which meet all the specified conditions. In the example at the top of this topic, the search will find all customers whose first name is 'CARL' and with a customer_type of 'R', plus the customers who have an 'S' in their last_name.
The column search conditions that can be specified are as follows
Condition |
What it does |
Example |
What matches example |
text |
column exactly matches text |
com |
com |
='text' |
This is an alternate way of specifing a column match. Useful if the text contains a comma. |
='com' |
com |
*text* |
column contains text |
*com* |
command, accomodation |
text* |
column starts with text |
com* |
com, command |
>value |
Column is greater than value. Other operators that can be specified are <, <= and >=. Value can be either a string value or a number. |
>20 >y |
21, 99, 4232 young, zoo |
a to b |
column is between a and b (this includes a and b). a and b can be string values or numbers. |
1 to 7 j to q |
1,2,3,4,5,6,7 jack, ken, peter |
null |
column is null |
|
|
blank |
column is blank. Same as ='' |
|
|
in (list of values) |
column is one of the values |
in (1,3,5,7) |
1,3,5,7 |
Other things you can specify:
not |
This selects all rows which do not meet the condition |
date |
Useful when comparing date values. date returns the current date |
now |
Useful when comparing timestamp values. Returns the current timestamp value |
You can specify multiple search condition by separating the conditions with a comma. The column meets these conditions if any of the conditions is met.
Example |
What it does |
ibm,*ca* |
column is either equal to ibm or contains ca |
=6,>20 |
column is equal to 6 or greater than 20 |
not 5 to 7 |
column is not between 5 and 7 |
Whether the searches are case dependent depends on your database. Databases such as Oracle and DB2 are case dependent, whereas databases such as SQL Server, Sybase, Access are case independent.
When you click on a cell, you get a button with three-dots at the right end of the cell. Clicking on this will get the values of the column in the table. For a large table, this could take a while to process. The list of values appears in the grid on the right (as in the example at the top of this topic).
Clicking on a value will create a search condition of this value. You can select multiple values (using the Shift or Ctrl keys) - this will build an IN clause for the column.
Clicking on this will show you all rows in the table (no search condition).
Clicking on this (or Ctrl-D) will clear the selected search. To clear all searches, select the menu item Clear > All Searches.
The Search Table function is designed as a simple window for building quick and simple searches. For building more complex searches you should use the Query Builder.