This tab is used to specify how the data in the Target table is loaded from the data in the load source.
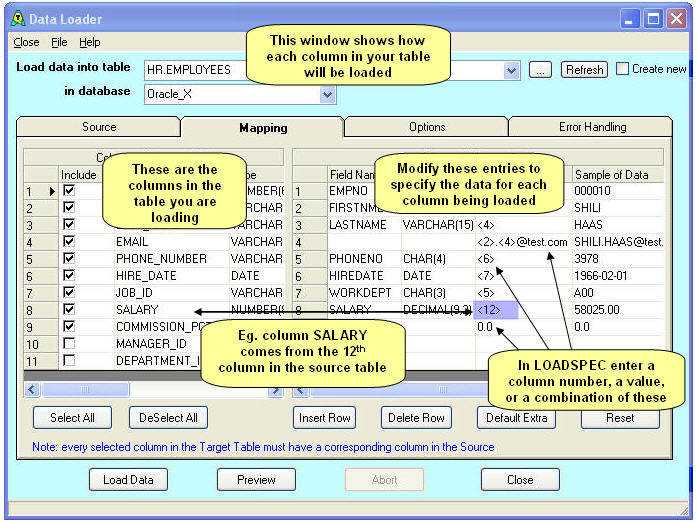
In the LEFT pane
In the RIGHT pane
Load Spec gives the Load Specification for the table column. By default this will be a value in angle brackets such as <4>, which means column 4 from the source. You can specify other things here to manipulate the data, for example:
0 |
Load the value 0 |
TEST |
Load the value TEST |
<3><4> |
Load source column 3, concatenated with source column 4 |
20<3> |
Load the string 20 followed by source column 3 |
<3:left(4)> |
Load the leftmost 4 bytes of source column 3 |
NULL |
Loads a null value |
The Load Spec can have any mixture of text and source column specifications.
The way AQT processes these is quite simple: AQT will scan the load spec and replace any source column specifications with the data from the source. The source column specification is in the format <colno> or <colno:func>. Func applies a function to the column value.
Valid functions that can be specified are:
lcase |
lowercase string |
ucase |
uppercase string |
scase |
sentence case (first letter of a word is upper case, rest is lower case) |
left(n) |
leftmost n characters |
right(n) |
rightmost n characters |
mid(m) |
rightmost part of string from character m |
mid(m,n) |
n characters starting from character m |
ltrim(x) |
trim character x from the start of the string. If x is not given (eg. ltrim), spaces are removed from the start. |
rtrim(x) |
trim character x from the end of the string. If x is not given (eg. rtrim), spaces are removed from the end. |
trim |
trim spaces from the start and end of the string |
date(datespec) |
converts dates, times and datetime values from one format to another. Described in more detail below. |
mask(mask) |
Provides a powerful way of manipulating data in a column. Described in more detail below. |
nib |
null if blank. If a blank value is specified, it is loaded as nulls. See also the Treat Zero-length Values as NULL option |
nis |
null if spaces. Similar to nib. See discussion later. |
rep(s,t) |
replaces all occurrences of string s with string t. Example: rep(Street,Road). See the section on Special Characters to see how to replace characters such as the comma, bracket etc. |
trans(a,b) |
translates string values. See discussion below. |
ifnull(s) |
returns value s if the input value is NULL. If you omit the (s) (eg. just have nullif), a zero-length string will be returned. |
ifblank(s) |
returns value s if the input value is blanks. |
ifempty(s) |
returns value s if the input value is a zero-length string. |
Let us know at support if there are any other functions that you might find useful (they are easy to implement).
Datespec
Datespec takes any string that Windows can interpret as a date or time, and formats it as defined by datespec. This is often a very useful function when copying data between databases of different types.
Datespec can be any combination of yyyy (year), mm (month), dd (day), hh (hour), nn (minutes), ss (seconds).
Example: date(yyyy-mm-dd) will convert 31/12/2003 to 2003-12-31.
Datespec can also be used to convert timestamps / datetime values from one format to another. To do this, both datespec and the values to be converted must be in a particular format. This is (for instance):
yyyy-mm-dd hh[colon]nn[colon]ss.xxx
where
Mask
This function provides a simple and powerful method for manipulating a string value. It is particularly useful for changing the order of values in a string.
You pass to the Mask function a mask string - this says how the data in the result string is to be formatted. The mask string consists of a series of characters:
The following table gives an example of how this is used.
Input Value |
Mask |
Resultant Value |
20041201 |
abcd-ef-gh |
2004-12-01 |
20041201 |
abcdghef |
20040112 |
2004-12-01 |
abcdfgij |
20041201 |
12-01 14:31:27 |
de-ab% |
01-12 14:31:27 |
Trans
The trans function is used to translate string values. In the example of trans(abc,def), AQT will replace all occurrences of a in the string with d, all occurrences of b with e, and all occurences of c with f.
Input Value |
trans |
Resultant Value |
this is a test |
trans(this,1234) |
1234 34 a 1e41 |
2004/12/01 12.23 |
trans("/.","-:") |
2004-12-01 12:23 |
[23] |
trans("[]","()") |
(23) |
$23,456 |
trans("$,",) |
23456 |
Special Characters
You can specify special characters using one of the following codes. It is useful to use these as some of these characters (quotes, brackets, colon) are used in the syntax of the load specs, so including them in a function can cause AQT to interpret the load spec incorrectly.
Code |
Value |
[squote] |
' |
[dquote] |
" |
[comma] |
, |
[semi] |
; |
[none] |
empty string |
[lbrak] |
( |
[rbrak] |
) |
[colon] |
: |
[dot] |
. |
[lf] |
line-feed. This is normal method of indicating a new-line for Unix files. |
[crlf] |
carriage-return+linefeed. This is normal method of indicating a new-line for Windows files. |
[tab] |
tab character |
Example:
Input Value |
Function |
Resultant Value |
12,34 |
rep([comma],[dot]) |
12.34 |
|
ifblank([squote]) |
' |
Include
If there is a column in your table from which you do not want data to be loaded, de-select the Include check-box for that column. The column will not be included in the load. Instead, the data will be taken from the default or auto-generated value for the column.
You can "string" a number of functions together. For instance:
<2:left(5):lcase>
This will do the left(5) on column 2, then do the lcase on the result.
You can string together up to 5 functions.
nis was introduced to deal with the following problem. Suppose you want to transform a date using mask, but to load null when the value is blank. You might try to code:
<2:mask(abcd-ef-gh):nib>
This doesn't do what you want; when <2> is blank <2:mask(abcd-ef-gh)> is ' - - ' which nib doesn't recognise as blank.
In this case use nis, eg: <2:mask(abcd-ef-gh):nis>. nis the same as nis except that it looks at the original value of the column <2> rather than the value as transformed by the previous function.